International Jurisdictions to Invest in India: A Comprehensive Guide
India has long been a magnet for foreign investment due to its rapidly growing economy, strategic location, and vast consumer base. For international investors, understanding the various jurisdictions that are favorable for investing in India is crucial. Certain jurisdictions not only offer tax benefits but also provide a smooth entry into the Indian market. In this article, we explore the best international jurisdictions for investing in India, the benefits and challenges associated with such investments, and the key sectors attracting foreign investment.
Why India is an Attractive Investment Destination
India is one of the fastest-growing economies in the world, with a large and youthful population, a growing middle class, and a strong digital infrastructure. These factors make India an attractive destination for foreign direct investment (FDI). The government has introduced several reforms, such as the Goods and Services Tax (GST), the Make in India initiative, and labor reforms, to ease the business environment. These factors, combined with a favorable democratic framework, make India a promising market for international investors.
Popular International Jurisdictions for Investing in India
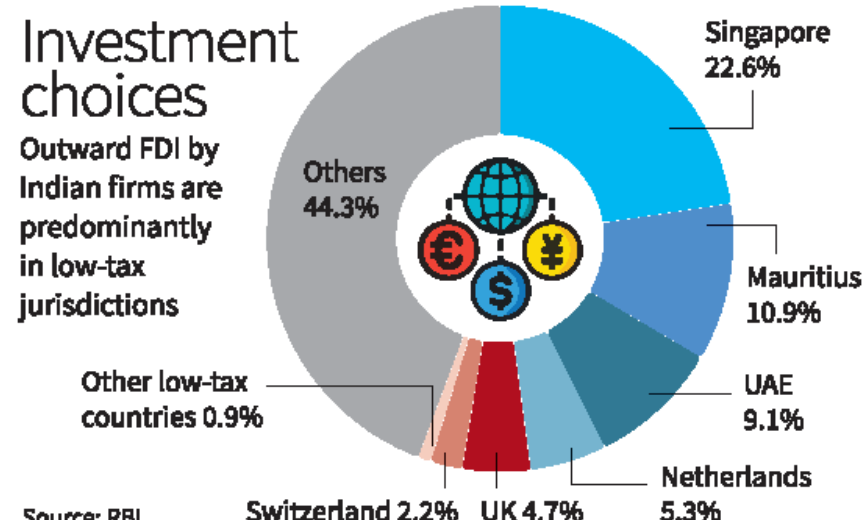
Several countries and jurisdictions are strategically positioned to facilitate investments into India. These include:
1. Singapore
Singapore is one of the most favorable jurisdictions for investing in India. The city-state offers an advanced financial infrastructure, efficient regulatory frameworks, and favorable tax treaties with India, which reduce tax liabilities for investors. Moreover, its proximity to India and thriving business ecosystem make Singapore a popular hub for international businesses seeking to enter the Indian market. The India-Singapore Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA) further strengthens the investment ties between the two nations.
2. Mauritius
For many years, Mauritius has been a preferred investment jurisdiction for foreign investors aiming to invest in India. This is largely due to the Mauritius-India Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA), which allows investors to avoid double taxation on income and capital gains. Additionally, Mauritius has a relatively low corporate tax rate and offers an efficient regulatory environment, making it a cost-effective route for international investors looking to capitalize on the Indian market.
3. United States
The United States is another major jurisdiction for foreign investment in India. As one of India’s largest trading partners, the U.S. benefits from strong economic and diplomatic ties with India. U.S.-based investors have easy access to various sectors in India, including technology, pharmaceuticals, and finance. The strong presence of U.S. multinational corporations in India, coupled with the India-U.S. bilateral trade agreements, enhances the ease of investment for American companies looking to expand into India.
4. United Kingdom
The United Kingdom continues to be a key player in India’s foreign investment landscape. India’s historical and cultural ties with the U.K., along with a large Indian diaspora in the country, have facilitated trade and investment flows. The India-UK FTA (Free Trade Agreement) is also expected to boost business ties further. British investors benefit from the India-UK DTAA, which offers tax relief on dividends, interest, and capital gains. The U.K. remains a top jurisdiction for investments in sectors like education, healthcare, and technology.
5. The Netherlands
The Netherlands has become an increasingly popular jurisdiction for foreign investment in India due to its favorable tax regime and business-friendly environment. Dutch investors benefit from the India-Netherlands DTAA, which allows for reduced tax rates on dividends, royalties, and interest. Additionally, the Netherlands has established itself as a gateway for businesses looking to access both the European and Indian markets, making it a strategic location for setting up holding companies.
6. Hong Kong
Hong Kong is a global financial hub that offers easy access to Chinese and Indian markets. Its low taxation system, along with its established financial infrastructure, makes it an attractive location for investors seeking to invest in India. The India-Hong Kong DTAA further helps investors mitigate double taxation on income and capital gains. The strong trade relationship between India and Hong Kong also provides a stable environment for foreign investments.
Key Benefits of Investing in India
Investing in India from international jurisdictions offers several advantages:
1. High Growth Potential
India’s growing economy, large population, and expanding middle class present significant opportunities for foreign investors. With a GDP growth rate consistently higher than many developed economies, India promises robust returns on investment, particularly in sectors such as technology, renewable energy, and consumer goods.
2. Strategic Location
India's position at the crossroads of Asia makes it a vital hub for businesses looking to expand in the region. Its access to the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and the broader Indo-Pacific region provides immense trade and investment potential for international businesses.
3. Government Reforms
India has undertaken numerous economic reforms to enhance the ease of doing business. The introduction of the Goods and Services Tax (GST), the Make in India initiative, and the Startup India program have made it easier for foreign investors to operate in the country. The Indian government is committed to creating a favorable environment for foreign investment through these initiatives.
4. Skilled Labor Force
India offers a large pool of skilled professionals, particularly in fields like technology, engineering, and finance. Foreign investors can benefit from relatively low labor costs while tapping into a highly educated and tech-savvy workforce, making India an attractive destination for outsourcing and offshoring operations.
Challenges of Investing in India
While India presents significant investment opportunities, foreign investors should be aware of potential challenges:
1. Regulatory Complexity
India’s regulatory environment can be complex, with a variety of rules that differ across states and industries. Navigating the various requirements related to taxes, labor laws, and environmental regulations can be time-consuming and requires careful planning.
2. Infrastructure Bottlenecks
Despite substantial improvements, India’s infrastructure still faces challenges, particularly in rural areas. Logistical delays and poor connectivity can hinder business operations, making it crucial for investors to conduct thorough due diligence before entering the market.
3. Political and Economic Risks
Political changes, regulatory shifts, and economic uncertainty can affect the business environment in India. However, India’s democratic governance and adherence to rule of law provide a relatively stable investment environment compared to many other emerging markets.
Conclusion
India remains one of the most attractive destinations for international investors, and understanding the right jurisdictions for investment is key to ensuring success. Jurisdictions like Singapore, Mauritius, and the United States offer distinct advantages in terms of tax benefits, regulatory frameworks, and ease of doing business. Despite challenges such as regulatory complexity and infrastructure issues, the opportunities for growth in India far outweigh the risks. With the right strategies and an understanding of the local market, international investors can unlock tremendous potential in this dynamic and diverse economy.

Comments
Post a Comment